When Darren got a wild idea a couple weeks ago to host a hand-water-pumping video contest, I had no idea where to start. Neither did he, but is a master at just winging it. First, he figured out the necessary, but mundane, logistics of uploading videos and drafting official rules and then announcing the contest.
Next came the fun part: Gathering prizes!
Darren got on the horn and started calling survival-related businesses. Much to our surprise and delight, many folks said, “Sure,” when he asked for a small donation. Among our generous donors is author and public speaker Rick Austin (The Survivalist Gardener), who even followed up with a telephone interview a few nights later.
Gardening is my favorite topic to study, so it was not easy to end our conversation, but I knew Rick had goats waiting to be milked. Here is a summary of the gardening tips Rick shared with me from his book, “Secret Garden of Survival – How to Grow a Camouflaged Food Forest.”
Incidentally, Rick has not planted a garden in years, yet he plops 3 to 6 gallons of fresh-picked fruit and vegetables every day onto the kitchen counter for preparing or storing.
Often, Rick’s gathering binges prompt his wife to say, “Stop! I can’t keep up with you,” as she readies the harvest for dehydrating, canning or eating.
How is that possible, you ask? Well, his technique is no longer commonplace, but it once was.
Outside their Appalachian off-grid home in North Carolina, the Austins carved out a completely natural, perpetual garden spot from the mature oak and pine forest. With the help of a hired bulldozer, in one afternoon they cleared a half acre right down to rock and red clay – the kind that turns to brick in hot, dry weather.
The Austins sold the hardwood, milled the pine for building materials and used the brush and rotted logs to construct berms for hillside terraces. Then, after all available soil was pushed into place, they began planting.
No straight, even, meticulously groomed rows of beans, corn and onions designate the area as a garden plot, however. In fact, whether from a distance or nearly atop the vegetation, it is almost impossible to realize a garden exists there at all. Which is precisely the idea, Rick said.
Rather than following traditional, modern plans that rely on planting annuals in Army-formation-style rows or boxy raised beds, the Austins instead mimicked nature and thousand-year-old harvesting methods. Before modern agriculture and invention of mechanized farm machinery, most of mankind foraged for food.
“Studies of native indigenous people around the world, people who have lived off the land for generations without electricity, without refrigeration, without commercial agriculture, and without pesticides and insecticides,” Rick said, “showed that these people have lived primarily on perennials as opposed to annuals such as your typical grocery store vegetables.”
In a future world where there is potentially no electricity, refrigeration, supermarkets, seed stores, fertilizers, pesticides and feed stores, it makes sense to look at people who have managed to live successfully for generations without these conveniences, he said.
As hunter/gatherers, people did not spend time planting and tending crops. They didn’t plant in rows. They didn’t plant year after year, didn’t weed, didn’t fertilize and didn’t water plants. Yet humans managed to survive for thousands of years this way.
“Straight rows are a haven for bugs,” Rick said, explaining why his produce grows in concentric circles, or guilds. At the center of each guild is a fruit tree draped in grape vines. Out from there, progressively shorter circles are formed of bushy plants, herbs and groundcover.
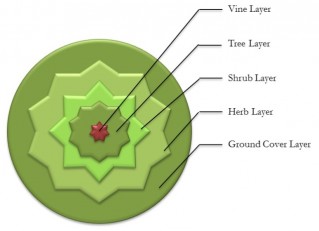 “With perennials, you plant once and harvest for a lifetime,” he said, adding that he spends only about an hour per day in the garden. Now in its fourth season, the garden yields more than the couple can possibly consume. Since they grow most of their own food, this is quite an accomplishment.
“With perennials, you plant once and harvest for a lifetime,” he said, adding that he spends only about an hour per day in the garden. Now in its fourth season, the garden yields more than the couple can possibly consume. Since they grow most of their own food, this is quite an accomplishment.
Of the few annuals incorporated into the garden, such as tomatoes, all are heirloom, allowing the Austins to save their seeds every year. Insects and weeds also are part of the scheme.
“Ninety percent of bugs are good bugs,” Rick said. “And weeds are ‘pioneer’ plants. They break up the soil.”
Learning to leave weeds in place was one of the greatest challenges for Rick’s wife, who must resist her lifelong inclination to pull every weed. Always, something is in bloom to attract beneficial insects, whether intentionally planted there or not.
Growing up with an apple orchard in New Hampshire, Rick was a typical apple-grower 30 years ago. The trees grew in geometrically straight rows with nothing between them but grass. Every 10 days and after every rain, Rick religiously sprayed each tree with expensive chemicals to ensure a quality harvest.
“I still had scabby, wormy apples,” Rick told me.
In time, Rick realized he not only was killing bad bugs, but also beneficial predator bugs, disrupting nature’s balance. Now, without any chemicals and by co-mingling plants to deter bad bugs, the Austins’ garden bears much more fruit without all the work or expense. Also, Rick said he is unsure why, but he is no longer afflicted with respiratory problems as he once was.
Rick said his theory about the positive effect of companion- and inter-planting became reality a few years ago when, after filling the garden area, he planted the leftover seed potatoes in a row elsewhere.
“They were doing really well,” Rick said. “They were nice, healthy plants. Then, one morning, I saw the first plant completely decimated, and the one next to it, and the next one.”
By the time Rick got to the fourth plant, the mystery was solved. A swarm of potato beetles was consuming the plants, readily moving from one to the next in the row. The bugs easily found the concentration of plants; and, compounding the problem, good bugs couldn’t compete with the mass of beetles.
 Inter-planting has other benefits. Rick noticed that the grapevines growing on fruit trees instead of trellises yielded more grapes. And, the apple and pear trees produced more fruit shrouded in grapevines. The list does not stop there, though.
Inter-planting has other benefits. Rick noticed that the grapevines growing on fruit trees instead of trellises yielded more grapes. And, the apple and pear trees produced more fruit shrouded in grapevines. The list does not stop there, though.
“We’re growing just about everything that will grow in this area,” Rick said, indicating peaches, plums, apricots and an assortment of nuts and berries that also fill the garden. He even is experimenting with citrus in a greenhouse built onto the south side of their home. “It’s like permaculture on steroids.”
Larger garden pests, such as rabbits, deer, raccoon and squirrels also are kept at bay with an arsenal of natural repellants. Perhaps the simplest is the dense barrier of blackberry bushes surrounding the garden site.
“Have you ever tried to walk through a patch of blackberries?” Rick asked.
My fascinating conversation with Rick lasted more than an hour. Check back for Part 2, Natural Pest Control, soon. For more on author Rick Austin, visit his facebook page.
Be sure to enter our hand-water-pumping video contest ongoing until July 23 for a chance to win a copy of the Secret Garden of Survival. Rick also is working on another book, the Secret Greenhouse of Survival.
Photos by Rick Austin



finished your book. excited to start. went out and bought 2 apple trees, 2 blueberry bushes and 2 muscadine grape vines. was told by local nursery that only muscadine grapes will grow here in Charleston Sc and should not plant with apple trees. what are your thoughts
Ray,
Thank you for your comment. You can write to author Rick Austin directly at Rick Austin, The Survivalist Gardener ; I know he’d love to hear from you!
Mrs. WaterBuck